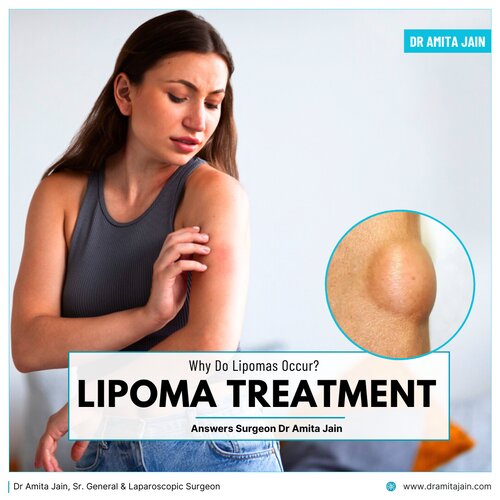
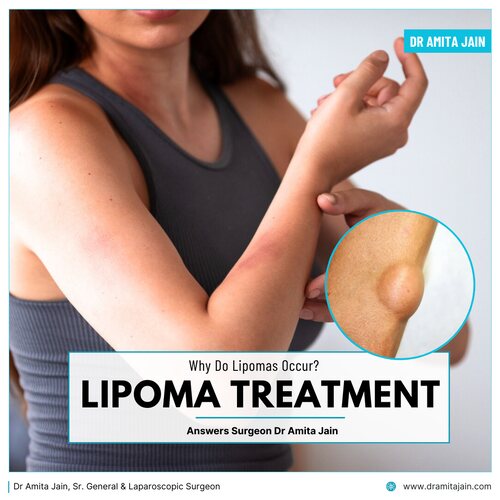
Discovering a soft lump under the skin can be worrying, especially when it seems to grow slowly over time. In many cases, these lumps turn out to be lipomas, a common and usually harmless condition. Lipomas often raise questions such as why they form, whether they are dangerous, and if they need treatment.
Understanding what lipomas are and why they occur can help reduce anxiety and guide people toward the right medical decisions, explains Dr Amita Jain, a senior experienced general and laparoscopic surgeon and one of the best lipoma specialist doctors in Delhi and India.
What Is a Lipoma?
A lipoma is a benign (non-cancerous) growth made up of fat cells. It develops just beneath the skin and feels soft, doughy, and movable when touched. Lipomas are generally painless and grow slowly over months or even years. They most commonly appear on the neck, shoulders, arms, back, abdomen, and thighs, though they can occur anywhere in the body where fat cells are present.
Lipomas can affect people of any age but are most frequently seen in adults between 40 and 60 years. They vary in size, ranging from a few millimeters to several centimeters. In rare cases, lipomas can grow quite large, but even then, they are typically not harmful.
Understanding Lipomas in Detail
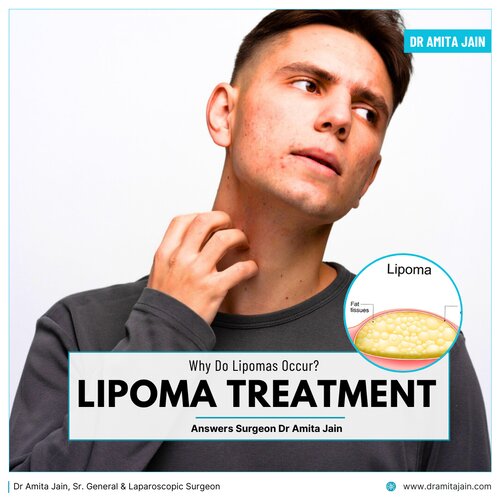
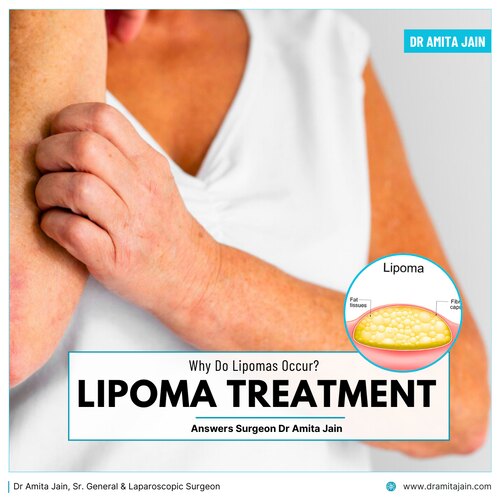
From a medical perspective, lipomas arise from an overgrowth of mature fat cells that cluster together and form a lump. Unlike cancerous tumors, lipomas do not invade surrounding tissues or spread to other parts of the body. They are usually well-encapsulated, meaning they are enclosed in a thin fibrous covering, which makes them easy to move under the skin.
Although most lipomas are painless, some can cause discomfort if they press against nearby nerves or are located in areas subjected to frequent movement or pressure. Variants such as angiolipomas (which contain blood vessels) or fibrolipomas (which contain fibrous tissue) may have slightly different characteristics but are still benign.
Why Do Lipomas Occur?
The exact cause of lipomas is not completely understood, but several factors are believed to contribute to their development, says Dr Amita Jain who is one of the highly experienced surgeons for lipoma in Delhi.
Genetic factors
Genetics play a significant role in lipoma formation. People with a family history of lipomas are more likely to develop them. Certain inherited conditions, such as familial multiple lipomatosis, cause individuals to develop multiple lipomas across the body.
Abnormal growth of fat cells
Lipomas occur when fat cells multiply abnormally in one localized area. This overgrowth is not related to overall body weight, which means even slim individuals can develop lipomas, while obese individuals may never have them.
Minor injuries or trauma
In some cases, lipomas have been observed to develop at the site of previous injuries or blunt trauma. While trauma does not directly cause lipomas, it may trigger fat cell proliferation in susceptible individuals.
Age-related changes
Lipomas are more common in middle age, suggesting that metabolic or cellular changes over time may contribute to their formation. As the body ages, the regulation of fat cell growth may become less precise, leading to localized accumulations.
Medical conditions and syndromes
Certain rare conditions, such as Madelung’s disease or Gardner’s syndrome, are associated with lipoma development. Additionally, metabolic disorders and hormonal imbalances have been suggested as contributing factors, though evidence is still limited.
Lifestyle and misconceptions
There is a common misconception that lipomas are caused by poor diet or lack of exercise. In reality, lifestyle factors have little direct influence on lipoma formation. Lipomas are not caused by eating fatty foods, nor can they be reduced through weight loss or exercise.
When Should You Be Concerned?
While lipomas are usually harmless, medical evaluation is recommended if a lump:
- Grows rapidly
- Becomes painful
- Feels hard or immobile
- Causes functional or cosmetic concerns
In such cases, a doctor may suggest imaging studies or removal to rule out other conditions.
Lipomas are common, benign fatty growths that occur due to a combination of genetic, cellular, and age-related factors. Although their exact cause is not fully known, they are generally harmless and do not pose serious health risks. Understanding why lipomas occur helps individuals recognize when reassurance is enough and when medical attention is necessary. With proper evaluation and guidance, lipomas can be managed safely and effectively, offering peace of mind to those affected.

Dr Amita Jain is one of India’s most distinguished and experienced female surgeons, known for her unmatched expertise in general and laparoscopic surgery. With over 29 years of surgical excellence, Dr Amita Jain has built a reputation for precision, compassionate care, and advanced surgical techniques.
Dr Amita Jain has successfully performed a wide range of complex general surgeries, including both open and minimally invasive procedures, with a strong focus on trauma care, onco-surgical techniques, and reconstructive surgeries. Her areas of specialisation include (including Gallbladder stone removal, appendix removal, hernia repair surgery, piles and fissure surgeries). She was the Professor of Surgery at the Army College of Medical Sciences and Base Hospital, Delhi Cantt. In 1994, she was commissioned asa Surgeon under the United Nations Mission in Congo. From 2020 to 2022, she worked with Bansals Hospital. Currently, Dr Amita Jain is the Senior General and Laparoscopic Surgeon at Rainbow Children Hospitals (Malviya Nagar, Delhi), Artemis Lite: Multi-Speciality Care Hospital (New Friends Colony, New Delhi) and at Rosewalk – Luxury Maternity Hospital in Delhi (Panchsheel Park, Delhi)
Call Us at +(91) 882-6615301